Powering the Immune System to Transform Lives
Our Platforms
Cutting-edge technology platforms to accelerate discovery and development
The powerful R&D engine of Vir Biotechnology is propelled by combining our expertise in antibody discovery with machine learning and artificial intelligence, specifically dAIsY™ (data AI structure and antibody), enabling us to optimize early drug candidates into impactful medicines. The PRO-XTEN™ masking technology could potentially make our future medicines more specific, effective and tolerable by making sure they act only where they are needed, reducing damage to healthy cells and tissue.
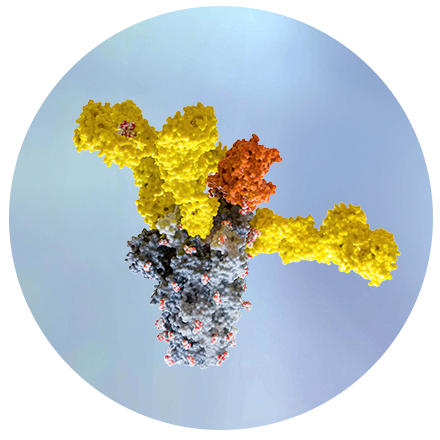
Next-generation antibody platform
Our antibody platform integrates proprietary discovery and protein engineering techniques to create impactful medicines.1, 2 Leveraging this platform, we are able to identify rare and broad antibodies and antibody fragments for viral and oncology targets with enhanced selectivity and potency. Using strategies such as artificial intelligence-led protein engineering with dAIsY™ (data AI structure and antibody), we can engineer our candidates to modulate interactions with the immune system and optimize key pharmacokinetic properties, such as half-life.
1 Pinto D. Park, YJ., Beltramello, M. et al. Cross-Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a Human Monoclonal SARS-CoV Antibody. Nature 583: 290–295 (2020).
2 Corti, D. et al. Protective monotherapy against lethal Ebola virus infection by a potently neutralizing antibody. Science 351: 1339-42 (2016).
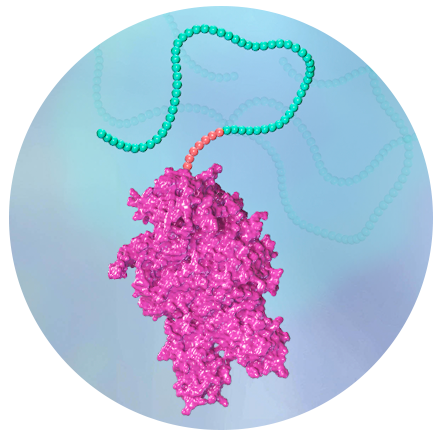
PRO-XTEN™ protease-releasable masking technology
PRO-XTEN™ masking technology enables drug candidates to become active (or unmasked) only where they are needed, in the tumor microenvironment, mitigating damage to healthy cells and tissue, and reducing toxicity.1 It also protects the candidates from the mechanisms that our bodies use to clear drugs from our system. This enables them to stay in the bloodstream longer and make sure they arrive at the site of action, potentially resulting in more convenient dosing regimens for patients and clinicians.2
Vir Biotechnology has exclusive rights to the PRO-XTEN™ masking platform for oncology and infectious disease. PRO-XTEN™ is a trademark of Amunix Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a Sanofi company.
1 For a selected publication, see: Cattaruzza, F. et al. Precision-activated T-cell engagers targeting HER2 or EGFR and CD3 mitigate on-target, off-tumor toxicity for immunotherapy in solid tumors. Nature Cancer 5:485-501 (2023).
2 Schellenberger V. et al. A recombinant polypeptide extends the in vivo half-life of peptides and proteins in a tunable manner. Nature Biotechnology 27(12):1186-1190. Podust V.N. et al. Extension of in vivo half-life of biologically active peptides via chemical conjugation to XTEN protein polymer. Protein Engineering, Design & Selection 26(11):743-753.
